Catalogue: Medical Encyclopedias
Encyclopedias
-
 Kitāb al-Zubdat al-ṭibb (MS A 81)
Kitāb al-Zubdat al-ṭibb (MS A 81) - (The Quintessence of Medicine)
- كتاب زبدة الطب
- by Ismā‘īl ibn Muḥammad al-Ḥusayn al-Jurjānī (d. ca. 1136/531 H)
- اسماعيل بن محمد الحسين الجرجانى
The Zubdat al-ṭibb (The Quintessence of Medicine) is a medical manual in synoptic chart format, written in Arabic. It is divided into two parts (qisms), the first on theoretical medicine in three books: the first book (kitāb) on diagnosis by pulse and urine and the causes and symptoms of disease, in three chapters (maqalahs); the second book on anatomy in two subsections (also called qisms); and the third book on fevers, in seven chapters (juz '). The second part (qism) of the treatise is on the treatment of diseases.
Not many copies of the treatise appear to be preserved. For other copies, see Richter-Bernburg, "UCLA", p. 7 note 69; GAL-S, vol. 1, p. 889; Ullmann, Medizin, p. 161 note 4; and Catalogue of Islamic Medical Manuscripts (in Arabic, Turkish, and Persian) in the Libraries of Turkey, ed. Ekmeleddin Ihsanoglu (Istanbul: Research Centre of Islamic History, Art and Culture, 1984), p. 182. see also Savage-Smith, "Bodleian", MS. Marsh 545 item 2.
Kitāb al-Zubdat al-ṭibb (MS A 81)
Illustrations
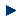
Synoptic charts concerning the anatomy of the upper and lower jaw (fakk), from the second chapter (bab) of the second book (kitāb) of the first part (qism) of Jurjānī's Kitāb al-Zubdat al-ṭibb (The Quintessence of Medicine). The copy is undated, possibly late 18th or 19th century.
Physical Description
Arabic. 81 leaves (fol. 1b-81a). Dimensions 29.7 x 20.5; text area 25.5 x 17 cm. The number of lines varies considerably from folio to folio, with a few sections running vertically. The title is given in the text (fol. 1b, line 21) as Kitāb al-Zubdat al-ṭibb. In the corner of fol. 1a a later hand has written: Dustur al-‘ilaj (The Register of Therapeutics), but then crossed it out. The author's name is given as Ismā‘īl al-Jurjānī on fol. 76b, line 1.
The copy is incomplete. The text stops abruptly on fol. 81a, during the discussion of therapy for melancholia. Fols. 75 and 76 are bound upside down; fol. 75 is bound out of order and should follow fol. 76.
The copy is undated. The appearance of the paper, ink, and script suggests a dating of the 18th or 19th century.
The copy is written in a medium-small (variable in size) naskh script. Black ink with headings in red. The text is written within frames of doubled red lines, and the charts are formed of red lines. There are catchwords. There are some marginalia and textual corrections.
There is a diagram of cranial sutures on fol. 30a. Nearly the entire treatise is in a diagrammatic format.
The cream lightly-glossed paper is fairly thick and has horizontal laid lines, single chain lines, and is watermarked. The paper is water damaged, and some folios have been repaired. The edges have been trimmed from their original size.
The volume consists of 81 leaves. Fol. 81b is blank. Fol. 1a is blank except for owner's stamps and signatures and an incorrect title (written in later hand), crossed out.
Binding
The volume is bound in a modern library binding of pasteboard covers and envelope flap, covered with red leather. There are modern paper pastedowns and endpapers.
Provenance
On fol. 1a there are two owners' stamps, with one impressed twice, and an illegible signature. There are also owners' stamps on fol. 1b (different from those on fol. 1a); the ones on fol. 1b are repeated on fols. 2a and 81a.
The volume was purchased in 1941 by the Army Medical Library, apparently from A.S. Yahuda.
References
Schullian/Sommer, Cat. of incun. & MSS., p. 324, entry A81.
NLM Microfilm Reel: FILM 48-127 no. 5
-
 Aghrāḍ al-ṭibb or al-Aghraḍ al-ṭibbīyah (MS P 1.1)
Aghrāḍ al-ṭibb or al-Aghraḍ al-ṭibbīyah (MS P 1.1) - (Medical Pursuits)
- كتاب اغراض الطب / كتاب الاغراض الطبيه
- by Ismā‘īl ibn Muḥammad al-Ḥusayn al-Jurjānī (d. ca. 1136/531 H)
- اسماعيل بن محمد الحسين الجرجانى
The Persian medical compendium by Jurjānī called Medical Pursuits (Aghrāḍ al-ṭibb or al-Aghraḍ al-ṭibbīyah) was composed after his more well-known Zakhīrah-i Khvārazm’Shāhī. It was intended as an introduction to the art of medicine, rather than a comprehensive encyclopedia of every aspect of the art as had been the intent of the Zakhīrah-i Khvārazm’Shāhī. It was composed for the minister (Majd al-Dīn Abū Muḥammad Sahib ibn Muḥammad al-Mukhari) to ‘Ala' al-Dīn Atsiz, the son and successor to Khvārazm’Shāh Qutb al-Dīn Muḥammad ibn Nushtigin. Medical Pursuits consists of two parts: the first part (bakhsh) is an abridgement of portions of the Zakhīrah-i Khvārazm’Shāhī, while the second bakhsh consists of 26 sections (guftars) concerned with the treatment of localized diseases.
For other copies, see Storey PL II,2, pp. 209-210; Richter-Bernburg, "UCLA", p. 19; Keshavarz, "Wellcome", p. 107-108; Catalogue of Islamic Medical Manuscripts (in Arabic, Turkish, and Persian) in the Libraries of Turkey, ed. Ekmeleddin Ihsanoglu (Istanbul: Research Centre of Islamic History, Art and Culture, 1984), p. 178; and Wilhelm Eilers and Wilhelm Heinz, Persische Handschriften, Teil I [Verzeichnis der orientalischen Handschriften in Deutschland, Band XIV,1] (Wiesbaden: Franz Steiner Verlag, 1968), p. 81 no. 91 and p. 234 no. 301. A facsimile of an extract from MS 4856 in Tehran University Central Library was published in Tehran in 1966 (Intisharat-i Bunyad-i farhang-i Iran 10, ‘Ilm dar Iran 3).
Aghrāḍ al-ṭibb (MS P 1.1)
Illustrations
The colophon from a copy of Jurjānī's Medical Pursuits (Aghrad al-tibb) that was copied in 1268 [= 1851-2] by a scribe whose name might tentatively be read as Rājah Rāmah.
Physical Description
Persian. 350 leaves (fols. 7b-356a). Dimensions 33 x 18.3; text area 24.3 x 12.5 cm; 19 lines per page. The title is given in the colophon on folio 356a (line 18 and in the margin) as: Kitab Aghrad al-tibb. A shortened form, Aghrad, occurs in the text at fol. 7a, line 4, and folio 180b, line 15. There is no title page. The author is not named. The treatise corresponds to that of other recorded copies, such as London, Wellcome Library for the History and Understanding of Medicine, MS Pers. 168 (Keshavarz, "Wellcome", p. 107) and Marburg, Staatsbibliothek, MS Orient. Fol. 3109, copied in 1334/734 H (Wilhelm Eilers and Wilhelm Heinz, Persische Handschriften, Teil I [Verzeichnis der orientalischen Handschriften in Deutschland, Band XIV,1] (Wiesbaden: Franz Steiner Verlag, 1968), p. 81 no. 91.
According to the colophon on folio 356a the copy was completed in 1268 [= 1851-2] by a scribe possibly named Rājah Rāmah, though the reading of that name is highly questionable.
The text is written in a medium-large shikastah script. Black ink with headings in red and occasional red overlinings. There are catchwords.
There is a tiny diagram of the optic chiasma in the margin of folio 27b.
The brown, semi-glossy paper has broad and wavy horizontal laid lines with traces of single chain lines; no watermarks were detected. The paper is soiled with grime and thumbing, and is waterstained at the upper corner.
The volume consists of 361 leaves. Fols. 1-6, 7a, 356b, and 357-361 are blank.
Binding
The volume is bound in a modern library binding of pasteboards covered with cloth, with a leather spine. There are modern endpapers and pastedowns.
Provenance
No information is available on its provenance or when it came into the collections of NLM. It was in the Armed Forces Medical Library by 1955, but was not included in the Schullian/Sommer catalogue.
References
NLM Microfilm Reel: FILM 55-42.1
-
 Risālah-i ḥifz al-ṣiḥḥah
(MS P 29, marginal item 3)
Risālah-i ḥifz al-ṣiḥḥah
(MS P 29, marginal item 3) - (An Essay on the Preservation of Health)
- رساله حفظ الصحة
- by Ismā‘īl ibn Muḥammad al-ḥusayn al-Jurjānī (d. ca. 1136/531 H)
- اسماعيل بن محمد الحسين الجرجانى
It is known from medieval sources that Ismā‘īl ibn al-ḥusayn al-Jurjānī composed a treatise titled Kitāb fi Ḥifz al-ṣiḥḥah (The Book on the Preservation of Health) in the year 1101/495 H. This is one of the few treatises which he apparently composed before moving to Khvarazm (see Richter-Bernburg, "UCLA", p. 6 note 53). Unfortunately no copies are known to be preserved today, so that it is uncertain whether the book was written in Arabic or Persian.
NLM has in its collections a small Persian treatise attributed to Jurjānī and titled: Risālah-i ḥifz al-ṣiḥḥah --- that is, "An Essay on the the Preservation of Health". The NLM copy is the only recorded copy of this Persian tract. It is possible that it consists of all or part of the otherwise lost Book on the Preservation of Health which Jurjānī wrote in 1101. It is also possible that the treatise is made up of extracts from the first part (that on the preservation of health) from Jurjānī's al-Aghraz al-tibbiyah (Medical Pursuits). Further analysis of the Persian treatise will be required before its relationship to other preserved works of Jurjānī can be firmly established.
Risālah-i ḥifz al-ṣiḥḥah (MS P 29, item 3 margin)
Physical Description
Persian. 8 leaves (fol. 3b-10b; marginal text). Dimensions 35.5 x 21; text area 31 x 4.5 cm. Text written diagonally in margins. The title Risālah-i ḥifz al-ṣiḥḥah is given in red as a title for the marginal treatise. The author is named near the start of the text itself as Sayyid Ismā‘īl ḥusayni Jurjānī.
The text, following the Basmalah begins: Muntajab-i Risālah-i ḥifz al-ṣiḥḥah (A Selection from the Essay on the Preservation of Health), suggesting that the tract preserved here may be only an extract of a longer treatise.
The text is written in the same hand as the main text in the volume. The manuscript is undated but signed by the scribe, Sayyid Ḥusayn Yazdī. There is a portrait of a scribe immediately below the colophon giving the scribe's name (fol. 173a). The volume must have been completed before 1546/953 H, when an owner's stamp for one ‘Imād al-Dīn Zakarīyā’ ibn Muḥammad ibn Maḥmūd Limūnī was placed in the volume. It appears to have been copied in India.
The marginal text is written in a small, compact, professional, and elegant
ta‘liq tending toward naskh script. Black ink with headings in red and red overlinings. There are catchwords for the central text, which is enclosed in frames of blue, red, gilt, and black lines. The marginal text is written in short diagonal lines between the frame enclosing the central text and a larger frame of blue, gilt, and black lines.
The glossy yellow-brown paper is moderately thin with only laid lines. There is some water damage near the edges, and the edges have been trimmed from their original size. Fol. 1 and 173 have been reinforced.
There are 173 leaves in the volume. Fols. 1a and 173b are blank. The main item in the volume, occupying the central text area of fols. 1b-173a is ‘Ajā’ib al-makhlūqāt wa-gharā’ib al-mawjūdāt by al-Qazwīnī (MS P 29). There are 35 distinct treatises written in the wide margins of the folios. The marginal items are: MS P 29, marginal item 1: (fol. 1b) Dar ḥaqīqat-i ‘ālam, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 2: (fols. 2a-3b) Risālah-i qiyāfah by Sayyid ‘Alī Hamdānī; MS P 29, margin item 3: (fols. 3b-10b) is here catalogued; MS P 29, marginal item 4: (fols. 10b-12a) Muqaddimah-i nabz, anon. ; MS P 29, marginal item 5: (fols. 18a-19b) Muqqadimah-i ‘ishq, anon. ; MS P 29, marginal item 6: (fols. 19b-22b) sharḥ-i pat , anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 7: (fols. 23a-25b) Dar ‘ishq, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 8: (fols. 26a-29b) Risālah-i ṭarīqah-i naqsh-bandīy, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 9: (fols. 33b-33b) on astronomical principles, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 10: (fol. 41a) on the zodiacal sign of Cancer, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 11: (fols. 42b-45a) on ancient authorities, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 12: (fols. 45b-46b) Ḥaqīqat-i ṭūl-i va ‘arḍ-i aqālīm, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 13: (fols. 52a-53b) on astrology and magic, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 14: (fols. 54a-56b) Risāla dar khāṣṣīyat-i zanān, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 15: (fols. 57a-62a) on magic squares and talismans, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 16: (fols. 62a-63b) Risālah dar hawāṣṣ, attributed to Ibn Sīnā; MS P 29, marginal item 17: (fols. 63b-66b) Muqaddimāt-i ḥisāb, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 18: (fols. 66b-70a) on numerology and lunar mansions, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 19: (fols. 70a-73b) on occult properties, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 20: (fols. 73b-77b) Muqaddimah-i raml, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 21: (fol. 77b) Muqaddimah-i ganjifah, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 22: (fol. 77b) Muqaddimah-i shaṭranj, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 23: (fols. 78a-80b) on magical alphabets, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 24: (fols. 81a-88b) Khulāṣah-i tawārīkh, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 25: (fols. 88b-91a) Khulāṣah-i rājāwatī, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 26: (fols. 92a-93a) on wonders among world rulers, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 27: (fols. 96a-99a) reports and sayings of learned Sufi shaykhs (untitled), anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 28: (fols. 99a-101b) Dar akhlāq-i ḥamīdah, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 29: (fols. 101b-108a) Tuḥfat al-wuzarā' , anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 30: (fols. 108b-109b) on magic, untitled, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 31: (fols. 114b-129a, 132a-140a, 141a-147a, 148a-162a) on medical-magical procedures (untitled) by Ibn ‘Abd al-Muṭṭalib; MS P 29, marginal item 32: (fols. 162a-165a) Risālah dar akl va shurb, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 33: (fol. 166a) Dar ḥisab-i siyāq-i ḥayawanāt, anon.; MS P 29, marginal item 34: (fols. 167a-167b) on compound recipes, untitled, anon.; and MS P 29, marginal item 35: (fols. 169a-172b) Khawāṣṣ-i jafrāt, anon. There are no marginal texts on fols. 12b-17b, 30a-31b, 34a-40b, 41b-42a, 47a-51b, 91b, 93b-95a, 110a-114b, 129b-131b, 140b, 141b-142a, 147b, 165b, 166b, 168a, 168b [only marginal corrections], and 173a.
Binding
The volume is bound in pasteboards covered with dark-brown leather. On the covers there are gold-tooled frames filled with acanthus leaves, with flowers or a star in the center and corners. The spine has gold-stamped flowers and a border. The binding is not original. There are modern pastedowns and endpapers.
Provenance
There is an owner's stamp dated 1546/953 H with the name ‘Imād al-Dīn Zakarīyā’ ibn Muḥammad ibn Maḥmūd Limūnī (fol. 173a).
The volume was purchased from R. Thomas Heller, New York, on 3 August 1949. No further information is available on the provenance.
References
NLM Microfilm Reel: FILM 55-41 no. 3












