



Table of Contents: 2012 JANUARY–FEBRUARY No. 384
Torre S. Versioning in PubMed. NLM Tech Bull. 2012 Jan-Feb;(384):e6.
PubMed now supports versioned citations. Revisions, scientific updates, and updates of reviews are examples of content that could be versioned. Versions are not intended for correcting specific errors in an article, for which published errata notices should continue to be used (see Fact Sheet).
The PMID of a versioned citation will remain constant while each version will have a unique version number assigned by PubMed. The combination of PMID and version number in the format PMID.version will be a unique identifier. All citations not versioned will be considered version 1.
There may be occasions when a specific version will be deleted. In these cases, the version number assigned to the deleted version will be skipped, and the next version of the citation will be assigned the following number. Version numbers will not be reused.
Version information is noted on the Summary, Summary (text), Abstract, and Abstract (text), displays. On the Summary display, the version number is located before the journal title abbreviation. The article’s original publication date is retained, and the version publication date is enclosed in square brackets (see Figure 1).

The Summary (text) display has a similar format (see Figure 2).

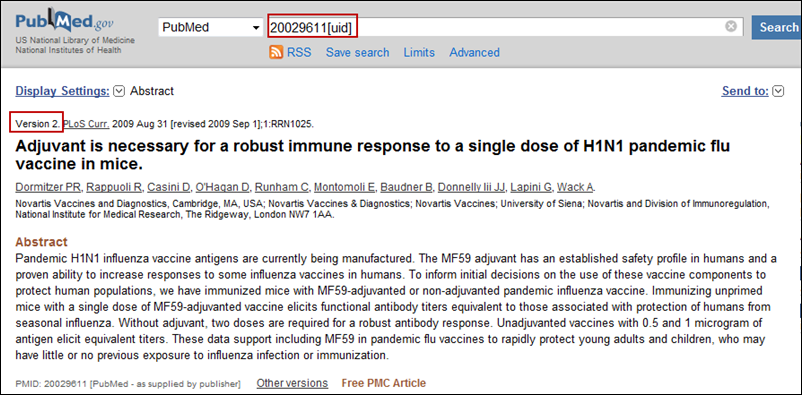
The Abstract display also indicates the version number and version publication date. Users can easily access prior versions of the citation by clicking on the "Other versions" link. A menu will appear listing all versions with the corresponding publication date. The version currently being viewed is in grey text and is not a link. All other available versions are links that will take the user to the Abstract display for that version (see Figure 3).


Only the most recent version of a citation will be indexed and returned in a PubMed search for a versioned PMID (see Figure 5). The content, e.g., author names, abstract terms, from previous versions will not be included in the PubMed indices. For example, if an author name has been removed from the author list in the most recent version, a PubMed search for that author name will not retrieve the citation. Users can access previous versions from the Abstract display or use one of the methods described below.
Search for a specific version of a citation by entering a PMID.version (e.g., 20029611.1) in the PubMed search box (see Figure 6). To search for multiple versions of a citation at once, use a Boolean OR (e.g., 20029611.1 OR 20029611.2).

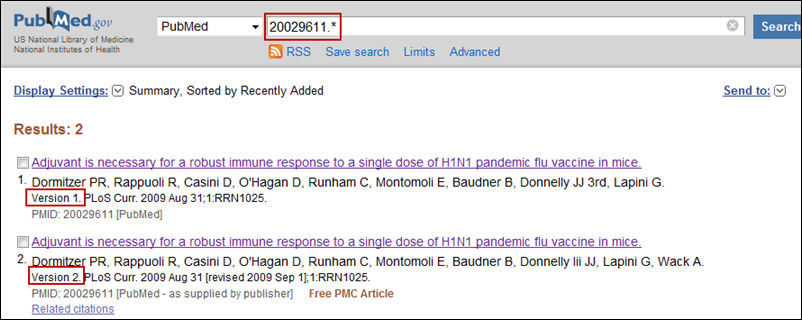
Search for all versions of a citation by entering the PMID followed by .* (e.g., 20029611.*) in the PubMed search box (see Figure 7).
PubMed will set the DateCreated for the new version to the date the citation is added to PubMed. We will retain the Entrez Date, which defines the display order in PubMed, as the original date unless the publisher supplies a new PublicationDate. If the PublicationDate on the new version is different, we will modify the Entrez Date so the citation will display at the top of the search results.
E-Search will only retrieve the latest version of a citation. E-Fetch can return a PMID.version.
By
Sarah Torre
National Center for Biotechnology Information