A recording of the original presentation is available.
Slide 1
PubMed Central Update
Jack Logue
MLA Conference
May 2008
Slide 2
What is PubMed Central?
- PubMed Central (PMC) is the U.S. National Library of Medicine's digital archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature
- A logical extension of NLM’s general mandate
- Provides free and unrestricted access
- Integrates journal literature with other valuable information resources in the NCBI database family (e.g., PubMed, Nucleotide, Protein)
- Digitizes journal back issues to create a complete electronic record of a journal
- Launched in February 2000
Slide 3
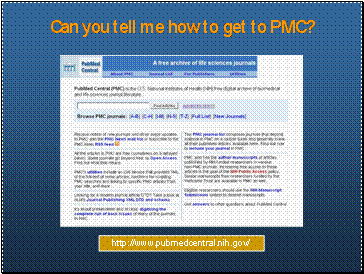
Can you tell me how to get to PMC?
Many ways to get to PMC:
[link removed] http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/
Slide 4

Can you tell me how to get to PMC?
- Most users search PubMed (or Google) to get to PMC articles
- It’s worth visiting PMC directly b/c not all articles in PMC have a PubMed record (out of PubMed scope).
Slide 5
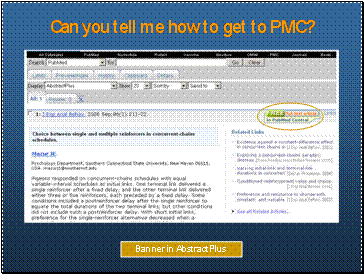
Can you tell me how to get to PMC?
- Using the Abstract Plus banner.
- You’ll also see the free article icon on PubMed search page
Slide 6
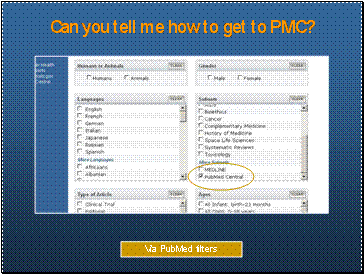
Can you tell me how to get to PMC?
- PubMed Limits includes PMC subset
- Translates to pubmed pmc local[ sb]
Slide 7
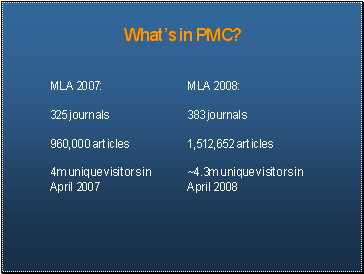
What’s in PMC?
MLA 2007: 325 journals, 960,000 articles, 4m unique visitors in April 2007
MLA 2008: 383 journals, 1,512,652 articles, 4.3m unique visitors in April 2008
- Substantial growth in offering AND usage continues at a rapid pace. Figures don’t include administrative materials (TOCs, covers, etc.)
- Public Access mandate has greatly increased publisher interest and applications.
- Will hit 1m articles later this spring. A great time was had by all as we congregated by the window. We had our cake…and then we ate it.
- 1 st quarter 2007: averaging ~3m unique IPs per month
Slide 8
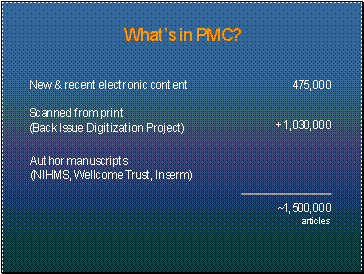
What’s in PMC?
~ 1,500,000 articles
New & recent electronic content: 475,000
= appx 1/3 of PMC content
Back issue scanning: +1,030,000
Very valuable resource to medical history searchers
great benefit to joining PMC – will discuss later
Manuscripts
basically: author manuscripts based on research funded by NIH, WT (UK), Inserm (France), some other grant funding agencies
I’ll get into how these sets of content differ later on. (Public Access has also impacted this significantly)
Slide 9
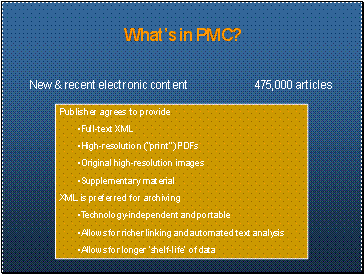
What’s in PMC?
New & recent electronic content: 475,000 articles
- Publisher agrees to provide:
- Full text XML
- High-resolution ("print") PDFs
- Original high-resolution images
- Supplementary material
XML is preferred for archiving
- Technology-independent and portable
- Allows for richer linking and automated text analysis
- Allows for longer "shelf-life" of data
PMC is not just a web site with journal articles
Xml/ sgml provided to us by publisher is converted to archival standard
Articles from across all the journals in the archive are standardized to the same archiving dtd
When user clicks to view article, html page is created ‘on the fly’ based on the standardized xml
It’s the standardized xml that really constitutes the archive
Can also analyse xml for better linking to other NCBI databases (to pubmed citations, taxonomy records, etc)
Soon will be able to point back to PMC from other NCBI dbs
Slide 10
What’s in PMC?
Back Issue Digitization Project: 1,030,000 articles
- Print journals scanned “cover to cover” (from earliest volume)
- Create and archive high resolution PDFs with true reproduction of figures/images
- OCR text used to do full text searched and build list of linked reference citations
Another great source of pride to PMC – and great benefit to searchers and publishers - to be able to include a journal ‘cover to cover’
High level of quality assurance
We apply high-level character recognition to be able to recreate and pull out reference citations
Major benefit to societies/publishers, who get to keep the entire run of scanned content (and distribute it to other archives)
Slide 11
What’s in PMC?
Example of reference citations, along with links we’re then able to generate pointing to PubMed records
Slide 12

To Join PMC…
Here’s what happens from publisher’s perspective:
- Formal agreement signed between NLM and publisher
- Journal may delay free access to up to a year or more
- Copyright is retained by publisher or author
- Publisher may designate journal (or certain articles) as open access
- Deposits are permanent: journal may stop depositing new content but may not withdraw content already deposited in PMC
Slide 13
Joined PMC in 2007/08
Acta Crystallographica Section F, molecular systems biology, Netherlands Heart Journal, Studies in Mycology...
~50 new journals joined PMC on a full participation basis last year. ~50-60 more currently in the evaluation pipeline. These will become available in a steady stream from now to the foreseeable future.
Many of these are from abroad. Centers in Korea, Eastern and Western Europe.
Slide 14
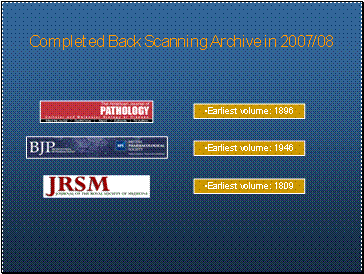
Completed Back Scanning Archive in 2007/08
The American Journal of Pathology (1896- ), British Journal of Pharmacology (1946- ), Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine (1809- )...
Some back scanning that was completed recently.
Back Scanning program currently not active, due to budgetary constraints.
From medical history standpoint, there’s very interesting content here
Slide 15
Forthcoming Scanning Projects
- BMJ + Specialist titles nearly complete.
- Journal of the National Medical Association
- But alas…funding is gone!
JNMA focuses on advancing the art of medicine for African-Americans.
JNMA founded as an alternative to JAMA because African Americans were not allowed to join the AMA at that time.
Flat budgets have sunk the scanning project!
Slide 16

OA Titles Joining PMC 2007/08
MDPI Marine Drugs, Environmental Health Perspectives, Yale Journal of Biology and Medicine, Clinical and Developmental Immunology, Metal-Based Drugs, International Journal of Plant Genomics
Total = 200+ journals with full or partial open access
OA = many journals are going beyond embargo-free and want to make they’re content as widely-available as possible.
Users benefit a couple of ways:
Articles immediately available (and in some cases distributable according to Creative Commons terms or whatever OA terms are on the article)
The metadata – and in some cases f/t - for OA articles in PMC is available for downloading (for citation analysis, etc). Some nice visualizations have been built using this data.
OA is a viable model. Hindawi is making a profit. Other publishers (like Bentham) are making an effort to also profit by this method.
Slide 17
Open Access Feeds
Blackwell Online Open, Springer Open Choice Articles, Taylor and Frances “ iOpenAccess” – coming soon
Nice arrangement whereby some publishers have agreed to provide their OA articles to us – whether or not the journals are full PMC participants.
Slide 18

Finding NCBI Related Records
Now let’s move on to some features
This is not a new feature, just a reminder of how one can link to other NCBI records from PMC article
Slide 19
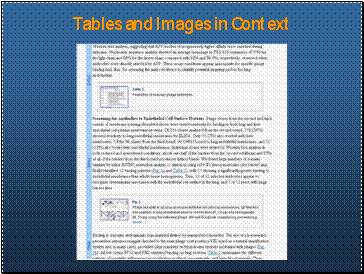
Tables and Images in Context
Moved tables and figures from back of article into the article body.
Slide 20
PMC Help on Bookshelf
A user’s guide to PMC is published on the Books site, as a part of the NCBI Help manual.
Slide 21

PMC News RSS Feed
Slide 22

UK PubMed Central (UKPMC)
Went live a few months ago
PMC mirror
Slide 23

UK PubMed Central (UKPMC)
Partnership btwn NLM and health agencies in UK
Has its own manuscript submission system for research funded by UK agencies – Bart will discuss
Slide 24
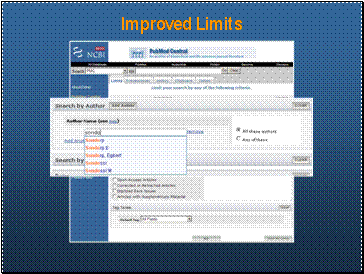
Improved Limits
Like PubMed limits, includes autocomplete on journal field and author field
Journal field reflects full PMC participating journals as well as journal manuscripts via NIHMS
Nice feature of author field is that since PMC indexes full names (when provided), you can see full names
Slide 25

Contact Us
PubMed Central: //www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov
Questions about PMC?: pubmedcentral@nih.gov
Last Reviewed: February 14, 2014

